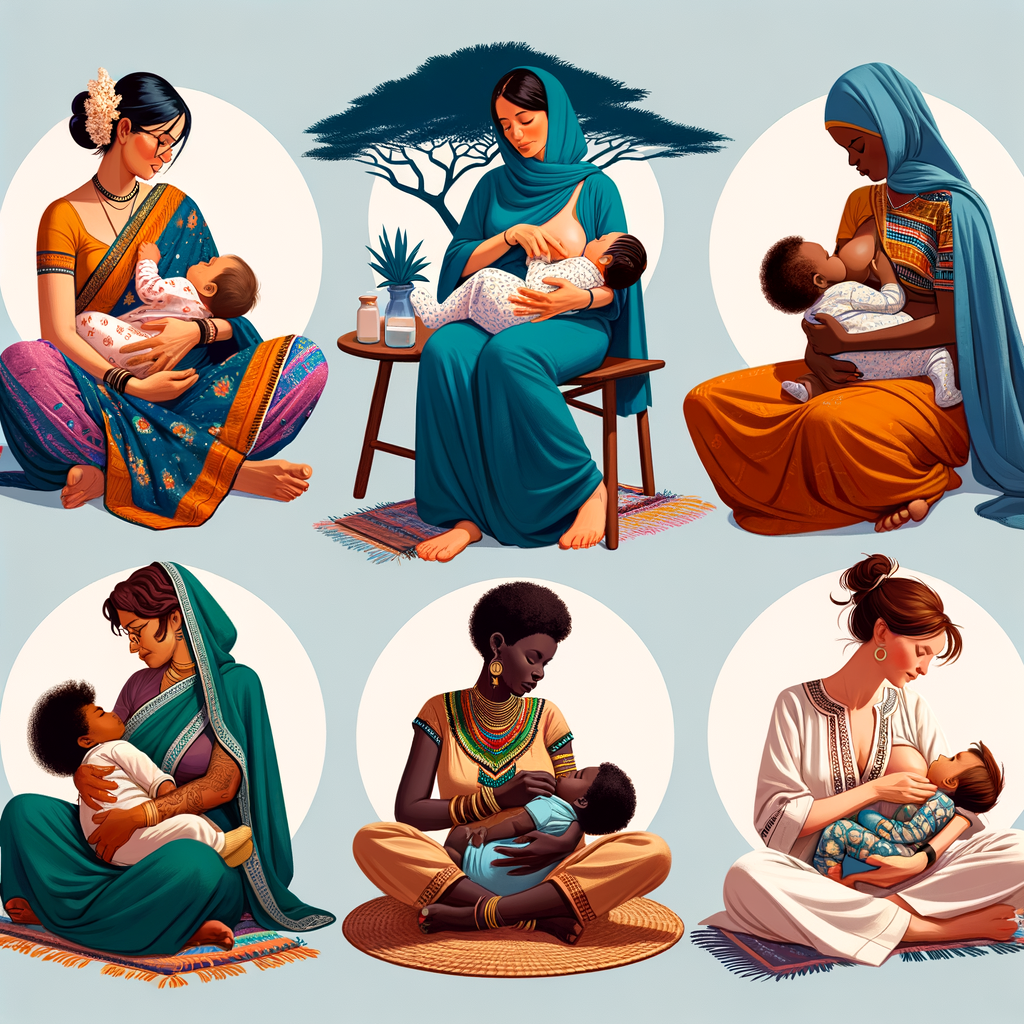
Introduction: Global Perspectives on Breastfeeding
Welcome to our exploration of breastfeeding practices from around the world. In this post, we’ll delve into the importance of understanding diverse breastfeeding practices and the global norms and variations that exist. We’ll also look at how culture influences these practices, and take a closer look at the differences that exist globally. By the end, we hope to provide you with key takeaways and a greater appreciation for the diversity in breastfeeding practices.
- Importance of Understanding Diverse Breastfeeding Practices
- Global Breastfeeding Norms and Variations
Understanding diverse breastfeeding practices is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it helps us appreciate the rich tapestry of human cultures and traditions. Secondly, it can provide valuable insights for healthcare professionals, enabling them to offer more culturally sensitive and effective support to new mothers. Lastly, it can help us identify best practices and innovative solutions to common breastfeeding challenges.
When it comes to breastfeeding, there are certain global norms. For example, the World Health Organization recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of a baby’s life. However, the way this guideline is implemented can vary greatly from one culture to another. In some cultures, for instance, mothers may breastfeed their children until they are several years old, while in others, breastfeeding may be supplemented with other foods at an earlier stage. These variations can be influenced by a range of factors, including cultural beliefs, economic circumstances, and access to healthcare and support.
In the following sections, we’ll dive deeper into these topics, exploring how cultural influences shape breastfeeding practices and examining the differences in breastfeeding habits around the world. So, let’s embark on this fascinating journey together!
Cultural Influence on Breastfeeding Practices
Understanding the cultural influence on breastfeeding practices is crucial in appreciating the diversity in parenting across the globe. In this section, we will delve into the breastfeeding customs of Western societies.
Western Societies
Western societies, including North America and Europe, have unique perceptions and practices when it comes to breastfeeding. Let’s explore these in detail.
- Perceptions and practices in North America
- European breastfeeding customs
In North America, breastfeeding is viewed as a natural and beneficial practice for both mother and child. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about 83% of U.S. infants are breastfed at birth. However, this rate decreases as the child grows, with only 57% still breastfeeding at 6 months.
Many factors influence these practices, including workplace policies, access to lactation support, and societal norms. For instance, the lack of paid maternity leave in the U.S. often forces mothers to return to work early, impacting their ability to breastfeed.
European countries have diverse breastfeeding customs, influenced by cultural beliefs, healthcare systems, and government policies. For example, in Norway, nearly 99% of mothers initiate breastfeeding, and 80% are still breastfeeding at 6 months. This high rate is attributed to the country’s strong public health policies supporting breastfeeding.
On the other hand, the United Kingdom has one of the lowest breastfeeding rates in Europe. A study found that only 34% of UK mothers are still breastfeeding at 6 months. This disparity highlights the significant influence of cultural and societal factors on breastfeeding practices.
In conclusion, Western societies have varied breastfeeding practices, influenced by a range of factors from government policies to societal norms. Understanding these practices can help us appreciate the diversity in parenting and promote better support for breastfeeding mothers worldwide.
Eastern Societies
When we explore the world of breastfeeding, we find that Eastern societies have unique traditions and habits. Let’s take a closer look at these practices in Asia and the Middle East.
- Asian Breastfeeding Traditions
In many Asian cultures, breastfeeding is seen as a natural and essential part of motherhood. It’s not just about nourishment, but also about building a strong emotional bond between mother and child.
In countries like China, for example, it’s common for mothers to breastfeed their babies for two years or more. This tradition is rooted in ancient beliefs about the health benefits of breast milk. In fact, the World Health Organization recommends this practice for optimal child health.
However, modern lifestyles and work commitments are challenging these traditions. Many Asian mothers now have to balance traditional expectations with the realities of their busy lives. Despite these challenges, breastfeeding rates in Asia remain relatively high compared to other parts of the world.
- Middle Eastern Breastfeeding Habits
Moving on to the Middle East, breastfeeding is also highly valued. In many Middle Eastern cultures, it’s considered a religious duty. Islamic teachings, for instance, encourage mothers to breastfeed their children for two years.
However, just like in Asia, modern life is changing these habits. Many Middle Eastern mothers now have to juggle work and family responsibilities. Despite these changes, breastfeeding continues to be a central part of child-rearing in the Middle East.
| Region | Traditional Breastfeeding Duration | Modern Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Asia | 2 years or more | Work commitments, modern lifestyles |
| Middle East | 2 years (encouraged by religious teachings) | Work and family responsibilities |
In conclusion, while traditions and habits vary, the importance of breastfeeding is universally recognized in Eastern societies. Despite the challenges brought by modern life, these cultures continue to value and uphold their breastfeeding traditions.
African Societies
When we explore the world of breastfeeding, we find that African societies have unique practices and norms. Let’s dive deeper into the breastfeeding norms of Sub-Saharan Africa and North Africa.
- Sub-Saharan Africa Breastfeeding Norms
In Sub-Saharan Africa, breastfeeding is considered a natural and essential part of motherhood. It is a common practice for mothers to breastfeed their babies for up to two years. This is due to the belief that breast milk provides the best nutrition for infants and helps strengthen their immune system.
| Key Facts about Sub-Saharan Africa Breastfeeding Norms |
|---|
| 1. Breastfeeding is initiated immediately after birth. |
| 2. Exclusive breastfeeding is practiced for the first six months. |
| 3. Breastfeeding continues along with complementary feeding until the child is two years old. |
- North African Breastfeeding Practices
North African societies also value breastfeeding. However, their practices differ slightly from those in Sub-Saharan Africa. In North Africa, breastfeeding is typically continued until the child is around 18 months old. Mothers often supplement breast milk with other foods starting from the age of six months.
| Key Facts about North African Breastfeeding Practices |
|---|
| 1. Breastfeeding is initiated within an hour of birth. |
| 2. Exclusive breastfeeding is practiced for the first six months. |
| 3. Breastfeeding continues along with complementary feeding until the child is 18 months old. |
These practices in African societies highlight the importance of breastfeeding in providing essential nutrients to infants and fostering a strong bond between mother and child. As we continue to explore breastfeeding practices around the world, we will find that while the methods may differ, the goal remains the same: to provide the best possible start in life for our children.
Differences in Breastfeeding Globally: A Closer Look
As we explore the world of breastfeeding, it’s important to understand how different cultures and societies approach this natural act. Let’s take a closer look at the practices in India, a country with a rich history and diverse traditions.
Case Study: Breastfeeding Practices in India
In India, breastfeeding is not just a health practice, but a tradition deeply rooted in its culture. However, the rapid pace of urbanization and modernization is influencing these practices.
- Traditional practices and beliefs
- Impact of urbanization and modernization
Traditionally, Indian mothers are encouraged to breastfeed their babies immediately after birth. Colostrum, the first milk produced, is considered ‘liquid gold’ due to its high nutritional content. Exclusive breastfeeding is promoted for the first six months, followed by the introduction of complementary foods along with continued breastfeeding.
With urbanization and modernization, changes are being observed in breastfeeding practices. More women are joining the workforce, leading to a decrease in exclusive breastfeeding. The availability of formula milk is also influencing the choice of feeding. However, efforts are being made to promote breastfeeding and provide facilities for lactating mothers in workplaces.
In conclusion, while traditional practices continue to influence breastfeeding in India, modernization is bringing about changes. It’s crucial to strike a balance between the two, ensuring the health and well-being of both mother and child.
Case Study: Breastfeeding in Scandinavian Countries
Scandinavian countries, namely Denmark, Norway, Sweden, and Finland, are known for their progressive approaches to many societal issues. This includes their approach to breastfeeding. Let’s take a closer look at how government policies and societal attitudes in these countries support breastfeeding.
- Government policies supporting breastfeeding
- Societal attitudes and acceptance
In Scandinavian countries, government policies play a significant role in promoting breastfeeding. For instance, mothers are entitled to paid maternity leave, which allows them to spend more time with their newborns and establish a strong breastfeeding routine. In Sweden, mothers can take up to 480 days of paid parental leave, with 90 days reserved exclusively for the mother. This policy not only supports breastfeeding but also promotes gender equality.
Moreover, the governments of these countries also provide free or subsidized healthcare, including lactation consultation services. This ensures that mothers receive the necessary support and guidance for successful breastfeeding.
Societal attitudes towards breastfeeding in Scandinavian countries are generally positive. Breastfeeding in public is widely accepted and is seen as a natural part of motherhood. This acceptance is reflected in the high breastfeeding rates in these countries. According to a study, approximately 98% of mothers in Norway initiate breastfeeding, and about 80% are still breastfeeding at six months.
Furthermore, workplaces in these countries are typically supportive of breastfeeding mothers. Many companies provide lactation rooms and flexible work schedules to accommodate breastfeeding needs. This societal acceptance and support significantly contribute to the high breastfeeding rates in Scandinavian countries.
In conclusion, the case of Scandinavian countries demonstrates how government policies and societal attitudes can significantly influence breastfeeding practices. These countries serve as excellent examples for other nations striving to improve their breastfeeding rates and support for mothers.
International Breastfeeding Habits: Key Takeaways
In our exploration of breastfeeding habits around the world, we’ve discovered a few key factors that significantly influence these practices. Let’s summarize the main points:
- The role of cultural beliefs and traditions
Culture plays a significant role in shaping breastfeeding habits. For instance, in some African cultures, breastfeeding is considered a sacred duty, and mothers are expected to breastfeed their children for two years or more. Conversely, in some Western societies, there is a trend towards early weaning due to lifestyle choices and work commitments. Understanding these cultural nuances is crucial in promoting breastfeeding globally.
- Influence of societal norms and attitudes
Societal norms and attitudes also greatly impact breastfeeding practices. In societies where breastfeeding in public is accepted and encouraged, mothers are more likely to breastfeed for longer periods. However, in societies where breastfeeding is seen as a private act, mothers may feel uncomfortable and choose to bottle-feed instead. Changing societal attitudes towards breastfeeding can help encourage more mothers to breastfeed.
- Impact of government policies and healthcare systems
Government policies and healthcare systems can either support or hinder breastfeeding. Countries with strong maternity leave policies, such as Sweden, tend to have higher breastfeeding rates. On the other hand, in countries where maternity leave is short or non-existent, mothers often struggle to continue breastfeeding. Similarly, healthcare systems that provide support and education about breastfeeding can help increase breastfeeding rates.
In conclusion, understanding the cultural, societal, and governmental influences on breastfeeding can help us develop more effective strategies to promote breastfeeding worldwide. By respecting and acknowledging these diverse practices, we can work towards a world where every mother feels supported in her breastfeeding journey.
Conclusion: Embracing Diversity in Breastfeeding Practices
As we wrap up our discussion on global breastfeeding practices, it’s essential to underscore the importance of embracing diversity. Different cultures have unique breastfeeding practices, and understanding these variations is crucial for global health initiatives. Let’s delve into why this is so important.
- Importance of respecting cultural variations in breastfeeding
Every culture has its unique approach to breastfeeding, shaped by traditions, beliefs, and societal norms. For instance, some cultures may encourage breastfeeding for longer periods, while others may introduce complementary foods earlier. These practices are deeply ingrained and respected within these communities.
Respecting these variations is not just about cultural sensitivity. It’s about ensuring that health interventions and policies are effective and well-received. By acknowledging and incorporating these cultural practices, we can create more inclusive and effective breastfeeding support programs.
- Need for global cooperation and understanding
Global cooperation and understanding are paramount in promoting optimal breastfeeding practices. This means learning from each other and sharing best practices. It’s not about imposing one ‘right way’ of doing things, but about finding common ground and working together for the health of mothers and babies worldwide.
For instance, a country with high breastfeeding rates might share its successful strategies with a country struggling to increase its rates. Conversely, a country with unique cultural practices might offer new perspectives and solutions that others hadn’t considered.
In conclusion, embracing diversity in breastfeeding practices is not just a nice-to-have; it’s a must-have. It’s the key to creating more effective, inclusive, and successful global health initiatives. Let’s respect and learn from our differences, and work together for the health of mothers and babies everywhere.